Electric cars are changing the way we think about transportation, offering an eco-friendly alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. But did you know that electric cars have existed for over a century? In this blog, we will learn about the history of the first electric car, its evolution, and how it laid the foundation for today’s modern electric vehicles.
A Brief History of the First Electric Car
The first electric car was invented in the early 19th century, long before the internal combustion engine became mainstream. In 1828, Hungarian engineer Enyos Jedlik created a small-scale electric motor that powered a small vehicle. However, it wasn’t until 1834 when American blacksmith Thomas Davenport created a more practical version of the electric vehicle (EV) using non-rechargeable batteries.
In 1884, English inventor Thomas Parker is credited with creating the first practical electric car powered by rechargeable batteries. In the early 1900s, electric vehicles were quite popular, especially in urban areas where pollution from gasoline engines was a growing concern.
The Rise and Fall of Early Electric Vehicles
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, electric cars became quite popular for their quiet operation and zero emissions. They were particularly favored by wealthy urban citizens who valued convenience, as electric vehicles were easy to start and did not require the hand-cranking required for gas cars.
However, the mass production of gasoline cars, most notably the Ford Model T in 1908, along with the discovery of cheap gasoline, led to the downfall of electric vehicles. Gas-powered cars could travel longer distances, and refueling was more convenient than the limited range and slow charging of early EVs.
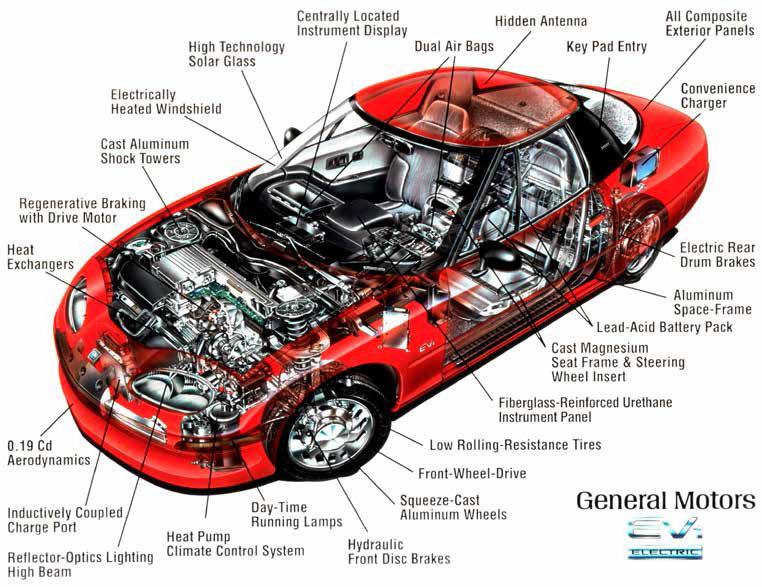
The Comeback: Modern Electric Vehicles
Fast forward to the 21st century, electric cars are making a strong comeback due to advances in battery technology and growing environmental concerns. Founded in 2003, Tesla played a key role in reviving the electric car market by introducing vehicles with extended range, innovative technology, and improved performance.
Why electric cars matter today
With the growing focus on climate change and reducing carbon emissions, electric vehicles are seen as a key solution to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. Modern EVs not only offer zero tailpipe emissions but also promise lower running costs, less noise pollution, and better energy efficiency than conventional vehicles.
Significant Dates in the invention of electric cars
The dates were researched from the internet, there might be a chance of missing any other information, which are not found on the internet, as a researching guide request reader’s, research more on books and individual institutions to know research more.
| Date | Invention/Advancement | Significance |
| 1881 | First Electric Vehicle | Thomas Edison creates a small, battery-powered vehicle. |
| 1897 | Electric Car Production | Production of electric cars begins in earnest, particularly in the United States. |
| 1908 | Model T | Henry Ford introduces the gasoline-powered Model T, which becomes the dominant automobile in the United States and eventually worldwide. |
| 1960s | Lead-Acid Batteries | Lead-acid batteries become the primary energy storage solution for early electric vehicles. |
| 1970s | Oil Crisis | The oil crisis renews interest in electric vehicles as a more energy-efficient alternative to gasoline-powered cars. |
| 1990s | Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries | NiMH batteries offer higher energy density and faster charging times compared to lead-acid batteries. |
| 1996 | General Motors EV1 | General Motors introduces the EV1, a limited-production electric car that helps popularize electric vehicles. |
| 2008 | Tesla Roadster | Tesla Motors launches the Roadster, the first commercially available electric sports car. |
| 2010s | Lithium-Ion Batteries | Lithium-ion batteries become the dominant battery technology for electric vehicles, offering higher energy density and longer range. |
| 2010s | Rapid Charging Infrastructure | Development of fast-charging stations expands the range and practicality of electric vehicles. |
| 2020s | Autonomous Driving Technology | Integration of autonomous driving features into electric vehicles begins, promising increased safety and convenience. |
| Ongoing | Battery Research and Development | Continuous research and development aim to improve battery performance, cost, and sustainability. |
The future of electric cars
Looking ahead, electric vehicles are expected to dominate the automotive market. With major automakers such as Tesla, Nissan, and Volkswagen investing heavily in electric vehicle technology, governments around the world are offering incentives to promote EV adoption. As charging infrastructure improves and battery technology advances, electric cars are set to become the norm, making the dream of sustainable transportation a reality.
The journey of electric cars, from their invention in the 19th century to their resurgence in the 21st century, highlights the incredible innovation in the automotive industry. As electric cars continue to evolve, they promise a cleaner, more sustainable future for generations to come.


